Acne Treatment in Mumbai - Sculpt Sublime (Plastic Surgery Clinic in Mumbai)
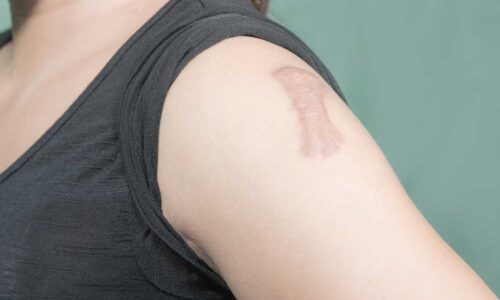
What is a hypertrophic scar?
A thick elevated scar is known as a hypertrophic scar. Extra connective tissue grows inside the initial wound area as a result of an aberrant wound healing response. Raised scar is the end consequence.
A minor cut on the surface of your skin usually heals without any problems. As the wound heals, fresh skin grows. Your body responds by creating collagen to mend deeper wounds (into the dermis layer and lower). Your skin’s collagen is thicker than the rest of it. This harder, less elastic tissue hardens into a scar. Scars are often flat. However, occasionally your body produces too much collagen, which causes a raised scar. Keloid or hypertrophic scars are both examples of this kind of elevated scar.
Where do hypertrophic scars commonly occur?
In parts of your body where your skin is tight, like your back, chest, shoulders, upper arms, elbows, and other joints, hypertrophic scars are more prevalent. Hypertrophic scars, however, can develop anyplace on your skin where there has been a skin injury or wound.
Scar tissue can develop as a result of skin damage, wounds brought on by trauma, inflammation, burns, and surgical incisions. There are other additional skin scar forms, each with a distinct appearance, aetiology, and remedy.
Are there risk factors that increase the chance of developing a hypertrophic scar?
Factors that increase the risk of hypertrophic scarring include:
- Burn wounds, especially second- and third-degree burns.
- Systemic (whole body) inflammation.
- Poor wound healing due to infection.
- Genetics. Raised scarring, especially keloids, run in certain families.
Are hypertrophic scars dangerous?
No, they are not harmful or potentially fatal. They mostly affect physical appearance and are aesthetic. Hypertrophic scars, however, might hurt or itch. You might wish to get them treated since they can restrict your movement if they develop over a joint.
What causes hypertrophic scars?
The three stages of wound healing include proliferation, remodelling, and inflammation. Throughout the remodelling stage, scar tissue develops. A number of distinct cell types, including fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, as well as specific signalling molecules, including tumour necrosis factor and transforming growth factor-beta, are all involved in tissue regeneration and wound healing. This healing reaction misbehaves in keloid and hypertrophic scars alike. These unwelcome thick, elevated, stiff scars are caused by an abnormal increase in collagen production and a decrease in elastin, even if the cause is not entirely known.
How are hypertrophic scars treated?
The objectives of treatment for hypertrophic scars are to flatten, soften, reduce the size, lighten the colour, and relieve any pain and itching that may be present. Before treating your scar, your healthcare professional, who is typically a dermatologist or plastic surgeon, may hold off for many months or perhaps a year. This gives the scar ample time to completely heal and may even cause it to shrink and flatten naturally.
The most common treatment options for hypertrophic scars include:
- Corticosteroid injections
- Laser therapy
- Bleomycin or 5-FU (fluorouracil)
- Injection Cryotherapy Surgery
FAQs
What is done in plastic surgery?
What is the difference between cosmetic and reconstructive surgery?
Cosmetic surgery is performed to reshape normal structures of the body in order to improve appearance and self-esteem. Cosmetic surgery is usually not covered by health insurance because it is elective.
Reconstructive surgery is performed on abnormal structures of the body caused by congenital defects, developmental abnormalities, trauma, infection, tumors or disease. In general, reconstructive surgery is performed to improve function, but may also be completed to approximate a normal appearance.
Reconstructive surgery is typically covered by most health insurance policies, although coverage for specific procedures and levels of coverage may vary greatly.
If I have Botox or Restylane, how often would I need to repeat the injections?
Botox lasts about three to four months, and the treatment can be repeated as needed. When it wears off, you will begin to notice increased muscle action and some reformation of the wrinkles. It appears that with repeated use, the effect of Botox becomes longer lasting.
Restylane injections last for about six months, and can also be repeated as needed.
How do I know what size breast implant is right for me?
The decision is based on a number of factors, including the patient’s desires, reasons for the surgery and overall health.
For example, are you doing it because you feel your breasts are too small relative to your body contour or are you unhappy with the size and firmness of your breasts following pregnancy, breastfeeding or major weight loss? Unevenness between the breasts can also be a motivating factor. Your surgeon can help you make the right decision during your pre-surgical appointment(s).